How Electrical Stimulation Is Used In Physical Therapy?

You may have come across the term “electrical stimulation” if you’ve ever visited a physical therapist to recover from a muscle injury or soft tissue injury. Or, if it’s a new term to you, let’s get familiar with the concept, and about how electrical stimulation may help alleviate the symptoms of various physical ailments.
What Is Electrical Stimulation?
The first scientific proof that electrical current could activate a muscle was given by Luigi Galvani in 1761. After that, various researchers studied the idea of Luigi Galvani. And these researches slowly and gradually led to the discovery of a painless procedure known as electrical stimulation.
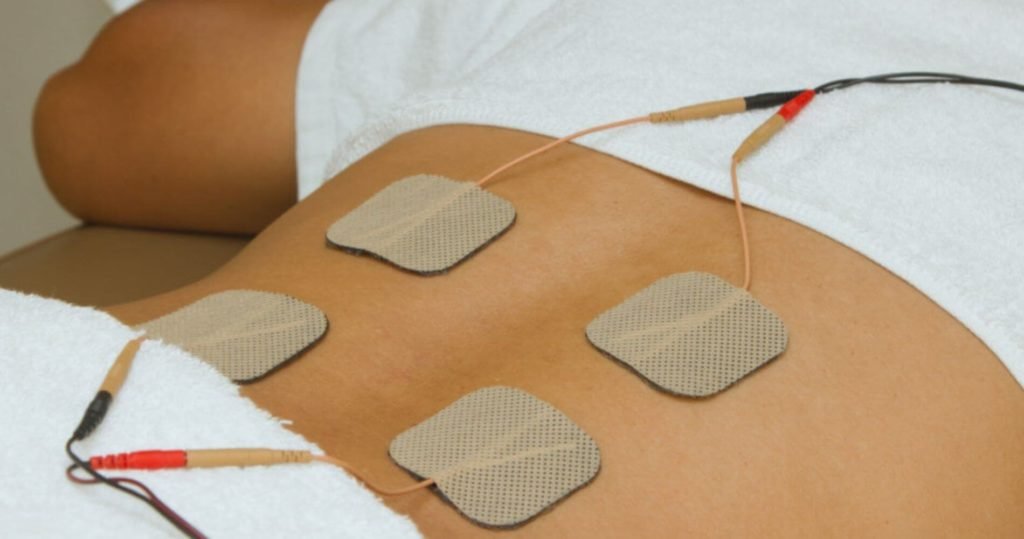
Electrical stimulation is a type of physical therapy treatment in which a mild electrical current is passed through the skin to repair injured muscles or manipulate nerves to reduce pain and to increase blood circulation.
What Does It Treat?
Electrical stimulation may work wonder for the patients with the following conditions:-
- Joint pain
- Arthritis
- Back pain
- Cancer-related pain
- Trouble swallowing
- Muscle conditioning
- Muscle injury
- Nerve inflammation
- Poor muscle strength
- Spinal cord injury
- Stroke
E-stimulation also trains the muscles to respond to the body’s natural signals to contract. This is especially helpful for stroke survivors who have to relearn basic motor functions. Electrical stimulation is also used to heal stubborn wounds. Now that we are aware of what electrical stimulation is, how it is discovered and what it does treat, we shall explore various types of electrical stimulation methods that are used to fulfill various tasks. Let’s read further to know more!
Various Types Of Electrical Stimulation
? TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation).
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) stimulates the nerves to relieve pain. It works exclusively on nerves rather than muscles.
? EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation).
Electrical Muscle Stimulation uses a slightly stronger current than TENS to stimulate the muscles to strengthen and rehabilitate them. Sportspersons like athletes and long-distance runners use EMS as a complementary technique for training.
? ESTR (Electrical Stimulation For Tissue Repair).
Electrical Stimulation For Tissue Repair (ESTR) aids in improving blood circulation, quickening wound healing, and lessening swelling.
? NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation).
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES) facilitates the nerves to prevent muscle atrophy. NMES exhausts the muscles, which helps in diminishing muscle spasms. This allows the muscles to relax.
? SCS (Spinal Cord Stimulation).
Spinal Cord Stimulation eases the lower back pain.
? IFC (Interferential Current).
The Interferential Current stimulates nerves to reduce pain, and relieve muscle spasms. It is used to calm the lower back pain.
? FES (Functional Electrical Stimulation).
In Functional Electrical Stimulation, a device is implanted in the body to preserve the functional and motor skills by providing the users with long-term stimulation.
How Does Electrical Stimulation Work?
- Small, sticky pads called electrodes are placed around the area receiving treatment. These electrodes are attached through a wire to the e-stimulation device.
- Wires attached to the electrical stimulation machine will deliver electrical pulses to the body.
- These electrical pulses block the transmission of pain signals from reaching the spinal cord and brain, and instead, send the signals to the targeted muscles to contract and relax.
- During this procedure, the patient will feel a slight tingling sensation which will increase as the procedure unfolds until it feels strong but comfortable.
- Each therapy session goes on from 5 to 15 minutes based on the ailment that is being treated.
- The repeated cycles of contractions and relaxations of muscles have the following effects:-
- An increase in blood circulation to the affected tissue area helps in repairing the muscles.
- By repetitive flexing, the general strength of weak muscles improves.
- It slows the process of muscles atrophy by strengthening the unused muscles.
- Training muscle fibers to respond in a certain pattern. For example, an athlete might use electrical stimulation therapy as a complementary technique to train muscles fibers to resist fatigue.
Risks Of E-Stimulation
- The most common risk of electrical stimulation is skin irritation underneath the electrode. If irritation happens then you should inform your therapist immediately so that the procedure can be stopped and a soothing lotion can be applied to the affected area.
- The next risk is a muscle tear. If the electrical pulse is too strong, then it may lead to the tearing of muscle tissue causing intense muscle pain.
- Electrical stimulation is not recommended for people with implanted heart devices or pacemakers as it can prove to be dangerous.
- E-stimulation is also not recommended for pregnant women. Although, in some supervised circumstances, e-stimulation has been used to help relieve labor pains.
Conclusion
Electrical stimulation has become a common and regular part of physical therapy for many ailments. But some studies indicate that e-stimulation doesn’t relieve pain very much, whereas other research reveals that some types of stimulation can be useful. There are anecdotal reports from patients who’ve claimed that they felt some relief from pain after the very first session of the therapy.
Despite the ongoing debate on whether e-stimulation truly helps or not, we should find out by ourselves whether we can benefit from this therapy.
Generally speaking, if administered correctly by professionals, these techniques are safe, painless can make a difference in pain levels, and can repair injured muscles.
These techniques when used for recovery, pain relief, or muscle training, should be supervised by professionals. However, there are some electrical stimulation devices available for home use that may be suitable in many cases.
The electrical stimulation procedure is not supposed to be painful, but if you experience any pain during the procedure, inform your doctor immediately so that they can adjust it properly or halt the treatment.
Last but not least, be sure to inform your doctor if you have any heart condition are pregnant or have an unhealed wound. Sharing your medical history, and your current medications, with your doctor, is a safe and intelligent approach.
PainPathways Magazine
PainPathways is the first, only and ultimate pain magazine. First published in spring 2008, PainPathways is the culmination of the vision of Richard L. Rauck, MD, to provide a shared resource for people living with and caring for others in pain. This quarterly resource not only provides in-depth information on current treatments, therapies and research studies but also connects people who live with pain, both personally and professionally.
View All By PainPathways